vol III Development:
Chapter 3: Cybernetics
page 1: Control
A system may be able to control itself if it has a defined ideal state, a means of measuring how near or far it is from that state, and a means of moving itself toward the defined state. The archetypal control system is the oven thermostat,
which turns up the heat when the oven becomes too cool and turns it
down when the oven becomes too hot. Control will be maintained if the
system is properly tuned and outside influences are not too strong.
An important function of cybernetics is to determine when control is
possible and what conditions are necessary to achieve it.
Perhaps the biggest technological breakthrough if the twentieth century is that, with the help of Claude Shannon and many others, we have learnt to measure information. Once we could measure it we could learn to control it and the result has been modern digital communicationn networks. As Shannon discovered, the key to control is digitization.
The essentials of a control system are shown in the illustration. The operator, which may be any particle or organism, senses information about its environment and uses this information to control its activity.
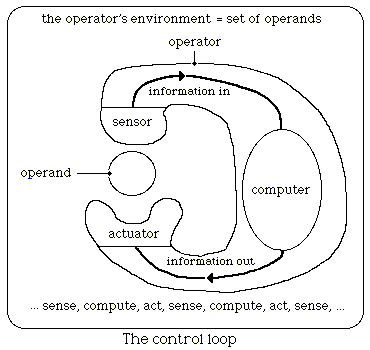
Normally a control system will have an ideal or set point. The sensing and computation function measures how far it is from its ideal and then devises the actions necessary for the actuator to bring it closer to the ideal. The ideal may be stationary or moving target. A sleeper, trying to remain warm and comfortable, can roll around and adjust the blankets to achieve their ideal. A tennis player trying to hit a ball will have to take both the motion of the ball and their own motion into account in order to play a satisfactory shot. Control theory - Wikipedia
The operator is part of its own environment, and may act on part of itself. One of the most important forms of activity is learning. By learning, one adds to the complexity of the structure one was born with, thus becoming capable of more complex acts of control. We see our children slowly learning to crawl, walk, speak and dress themselves as they get older and master more and more skills. Learning - Wikipedia
By learning more about itself and its environment, an operator can
improve its responses and reach its goals more efficiently. So we
find the mortality of young creatures is disproportionately high until
they gain the experience and strength to better secure their
survival.
The theological purpose of this site is to improve the responses of the organisms we call bodies politic, 'ships of state' or human communities. To do this, we seek to improve the sensors, computers, actuators, and communication links within our community. Our lives depend upon our ability to deal with our natural and human environment, avoiding death and obtaining the resources for growth and reproduction. Theology, the traditional theory of everything, provides us with the broadest level of guidance in this task. Governance - Wikipedia
Theology embraces all the sciences and all human experience, giving us an overall picture of the space in which we live with its social and technical problems. It plays the same role as the stars in celestial navigation, giving us reference points to show us where we are in divine and human space. Celestial navigation - Wikipedia
Error
The control loop is motivated by the difference between the goal
of its activity and the current situation. This distance is often called
the error signal. In the simple but practically important case of an
engine controlled by a governor, the error is the difference between
the actual speed of the engine and the desired speed. If the speed is
too low, power must be increased to bring the engine up to speed. If
the speed is to high, power must be decreased.
The social errors to which we must respond are much more complex,
things like poverty, disease, violence and ignorance. The desired
state is easy enough to contemplate, common wealth, health, peace and
awareness, but the means to bring it about are problematic.
Industrial and technological experience with the control of ever more
complex systems, however, gives us some clues.
We concentrate here on two principles or laws. The first, called by W Ross Ashby The law of requisite variety, states that if one system is to have control of another, the controller must be at least as complex as the system controlled. If this is not the case, the controlled system will have degres of freedom of which the controller is unaware and cannot control.W Ross Ashby
The other principle, which I call the principle of balanced devolution follows from the law of requisite variety. The demands on a system which controls a number of subsystems can be minimised (and its chances of success maximised) by maximising the autonomy of the subsystems. Devolution - Wikipedia
Divide a large system into small systems, each of which takes care of itself within the limits of its own knowledge and power. Divide small systems into still smaller systems, utilising the same principle. Then when we come to contruct a larger system, we do not need to know the details of the smaller systems. All we require is that they can be relied upon to play their part in the overall picture and to complain if they are being overstressed.
This principle holds in the physical world, where tiny systems like atoms take care of themselves while providing a foundation to build people, planets, galaxies and all the other wonderful structures that surround us. It also holds in a free and just society where each person is given maximum control over their
own affairs and the system responds quickly when an individual is overstressed.
A system may be optimised by adjusting the balance between central and local control in order to minimise the overall cost of control while maximising its finesse or gentleness. With these ideas in mind, we can then turn to searching for the sweet spot between totalitarianism and anarchy. My guess is that this is tantamount to what we call wilderness.
Both these ideas are consistent with the layered structure of computer networks. From the point of view of variety, higher more complex layers are able to control lower simple layers. The whole idea of network layering is built around the idea of devolution, making the lower layers relatively autonomous so that higher layers can use the facilities provided by the lower layers without having to micromanage them. Micromanagement - Wikipedia
These principles are illustrated in our own bodies. We are built as a hierarchy of systems running through fundamental particles to atoms, molecules, cells, organs and systems of organs to our overall selves controlled by the central nervous system and ultimately our conscious minds. When simpler systems break down, they must be repaired by higher and more complex systems. When our problems become to large to manage for ourselves, we have to seek help from higher social and technical layers like the health system or the justice system. Physiology - Wikipedia
(revised 6 January 2019)
|
Copyright:
You may copy this material freely provided only that you quote fairly and provide a link (or reference) to your source.
Further reading
Books
Click on the "Amazon" link below each book entry to see details of a book (and possibly buy it!)
Ashby, W Ross, An Introduction to Cybernetics, Methuen 1964 'This book is intended to provide [an introduction to cybernetics]. It starts from common-place and well understood concepts, and proceeds step by step to show how these concepts can be made exact, and how they can be developed until they lead into such subjects as feedback, stability, regulation, ultrastability, information, coding, noise and other cybernetic topics'
Amazon
back |
Barnett, S, and R G Cameron, Introduction to Mathematical Control Theory, Clarendon Press 1985 Jacket: '... This book remains the concise readable account of some basic mathematical aspects of control, concentrating on state-space methods, and emphasizing points of mathematical interest. ... '
Amazon
back |
Flannery, Tim F, Throwim Way Leg : Tree-Kangaroos, Possums, and Penis Gourds-On the Track of Unknown Mammals in Wildest New Guinea , Atlantic Monthly Press 1998 'An enthralling introduction to the mountain people of New Guinea - unimaginably remote, charming, cunning, cruel, subtle and appealing - and to their magnificent land.' New York times Book Review.
Amazon
back |
Gould, Stephen Jay, Life's Grandeur: The Spread of Excellence from Plato to Darwin, Jonathan Cape 1996 'We can and should appreciate human glory in human spheres. But any rational view of nature tells us that we are a single branch on an immense bush; and that life on earth is remarkable not for where it is leading, but for the fulness and constancy of its variety, ingenuity and diversity'
Amazon
back |
Leiss, William, The Domination of Nature, George Braziller 1972 'Among the questions posed at the beginning are the following: What are the concrete objectives sought in the human conquest of nature? What considerations governed the choice of science and technology as the means by which this conquest was to be accomplished? And what is the actual relationship between social progress on the one hand, and scientific-technological progress on the other?'
Amazon
back |
Leiss, William, The Domination of Nature, George Braziller 1972 'Among the questions posed at the beginning are the following: What are the concrete objectives sought in the human conquest of nature? What considerations governed the choice of science and technology as the means by which this conquest was to be accomplished? And what is the actual relationship between social progress on the one hand, and scientific-technological progress on the other?'
Amazon
back |
Lovelock, James, Ages of Gaia: A Biography of our Living Earth, W W Norton 1995 'This book describes a set of observations about the life of our planet which may, one day, be recognised as one of the major discontinuities in human thought. If Lovelock turns out to be right in his view of things, as I believe he is, we will be viewing the Earth as a coherent system of life, self regulating and self-changing, a sort of immense living organism.' Lewis Thomas
Amazon
back |
Midgeley, Mary, Beast and Man: The Roots of Human Nature, Routledge 1978-1995 'Philosophers have traditionally fastened on the qualities that make human beings different from other species. MM, drawing on the findings of ethology, stresses similarities. What makes people tick? To a greater extent than we yet understand, she says, the same things that make wolves and bears and elephants tick'
Amazon
back |
| Ritchie, Rod, Seeiong the Rainforests in 19th-century Australia, Rainforest Publishing 1989 'Sources [of the images and texts examined here] included expedition journals, settlers' guides, historical and botanical records, popular illustrated newspapers, travellers' narratives, picture books and tourist publications, paintings, drawings and photographs. The reproduction of this material provides an interesting and revealing insight into the many different ways the rainforests were seen.' [p 9]back |
Wannenburg, Alf, and Peter Johnson and Anthony Bannister (photography), The Bushmen, Chartwell Books Inc 1979 'Even as this book goes to press, the last of the Kalahari Bushmen are being drawn into the vortex of our civilisation. Aware of the urgency of the task, the author and photographers searched deep into the Kalahari thirstlands to find those few remaining Bushmen who still live as their forefathers have done for the last 20 000 years'
Amazon
back |
Wolpert, Lewis, The Triumph of the Embryo, Oxford University Press 1992 'Essentially the same mechanisms that are used in embryos are used by those animals that can, for example, regenerate their limbs. Thus there is a chapter on regeneration. Similarly there are chapters on growth and ageing, since both are related to embryonic development. Again, there is a short chapter on cancer, treating is as an an abnormal developmental process. Finally the role of development in evolution is given some attention.' [p vi]
Amazon
back |
Papers
| Platt, Michael L, Paul W Glimcher, "Neural correlates of decision variables in parietal cortex", Nature, 400, 6741, 15 July 1999, page 233-238. 'Decision theory proposes that humans and animals decide what to do in a given situation by assesing the relative value of each possible response. ... Our data indicate that a decision-theoretic model may provide a powerful new framework for studying the neural processes that intervene between sensation and action'. back |
Links
| Celestial navigation - Wikipedia, Celestial navigation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 'Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the ancient art and science of position fixing that enables a navigator to transition through a space without having to rely on estimated calculations, or dead reckoning, to know his or her position.' back |
| Control theory - Wikipedia, Control theory - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 'Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems with inputs, and how their behavior is modified by feedback. The usual objective of control theory is to control a system, often called the plant, so its output follows a desired control signal, called the reference, which may be a fixed or changing value.' back |
| Devolution - Wikipedia, Devolution - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 'Devolution is the statutory granting of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to government at a subnational level, such as a regional, local, or state level. It is a form of decentralization. Devolved territories have the power to make legislation relevant to the area.' back |
| Governance - Wikipedia, Governance - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 'Governance refers to "all processes of governing, whether undertaken by a government, market or network, whether over a family, tribe, formal or informal organization or territory and whether through laws, norms, power or language." It relates to processes and decisions that seek to define actions, grant power and verify performance.' back |
| Learning - Wikipedia, Learning - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 'Learning is the act of acquiring new, or modifying and reinforcing, existing knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, or preferences and may involve synthesizing different types of information. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals and some machines.' back |
| Micromanagement - Wikipedia, Micromanagement - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 'In business management, micromanagement is a management style whereby a manager closely observes or controls the work of subordinates or employees. Micromanagement generally has a negative connotation.' back |
| Physiology - Wikipedia, Physiology - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 'Physiology (from Ancient Greek φύσις (physis), meaning "nature, origin", and -λογία (-logia), meaning "study of") is the scientific study of normal function in living systems. A sub-discipline of biology, its focus is in how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system.' back |
|